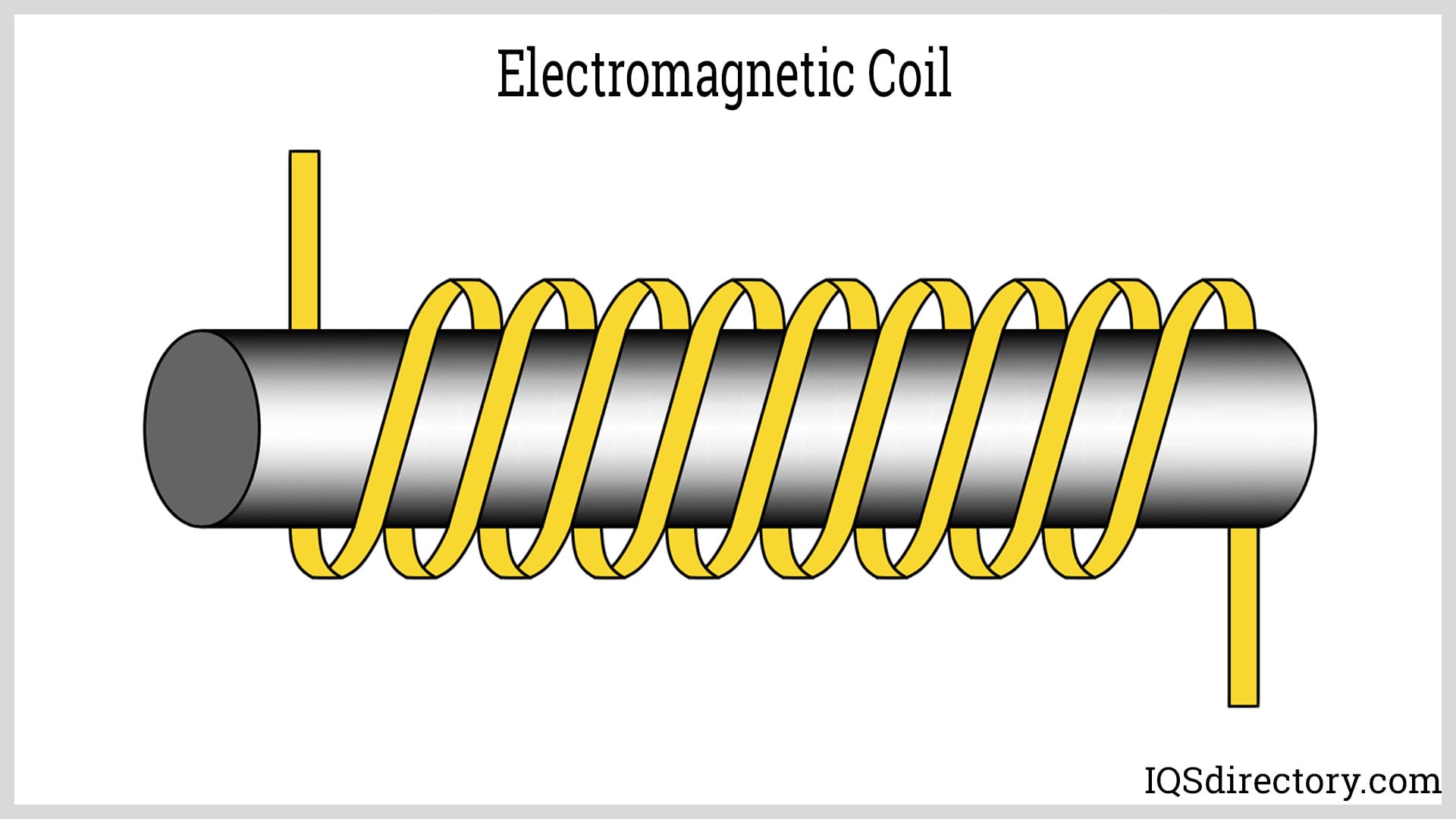
A toroid coil is a coil of coated or insulated wiring wound on a circular-shaped structure made from powdered iron. It is commonly used as an inductor in electric connections and very low frequencies where very large inductances are necessary. Read More…
We are proud of the craftsmanship of our engineers. All of our products are made right here in the United States and we promise that these items are created from high quality resources. Our electrical coils are unique and efficient.

Established in 1973, Classic Coil Company is a Contract Manufacturer of electronic coils. We manufacture coils for a variety of industries; winding wire gauges from 4-58 AWG. We are ISO 9001-2015 certified, ITAR registered and DFARS Compliant. Our Engineering services allow us to assist with design, reduce cost, and increase efficiency in production. Call or visit our website to learn more about...

Since 1962, Torelco has been a supplier of electric coils and transformers of superior quality. We offer custom coils, solenoid coils, ferrite core coils & toroid wound coils to serve a range of industries. Markets served include medical, military, electronics, and industrial. When you work with us, our promise is to build to the exact specifications and meet the custom needs of our customers.

Check out what’s new online at Precision Econowind, manufacturer of the highest quality custom coils at reasonable prices, with on time delivery. Serving the coil industry for over 30 years, we’re experienced with producing loudspeaker & medical industry coils, coils wound on customers’ bobbins/tooling; freestanding, flat wire, edge wound, square, rectangle & shaped coils. Submit your specs ...

Triad Magnetics has been in the electric coils industry for over 75 years. Giving us the knowledge and expertise to be one of the best in the industry. We have a wide range of electric coils and inductors as well as the ability to custom engineer and manufacture electric coils to our customer’s needs. Having served the needs of many industries for more than half a century, Triad believes its...

More Toroidal Coil Manufacturers

Toroidal Coils: Comprehensive Guide to Types, Applications, and Sourcing
Toroidal coils, also known as toroid inductors or toroidal transformers, are a cornerstone of modern electrical engineering and power electronics. Characterized by their doughnut-shaped (toroid) cores, these coils offer unique electrical properties that make them essential for efficient energy transfer, electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression, and compact design in a wide range of electronic devices. Whether you are searching for information on toroidal coil types, their primary applications, or best practices for sourcing high-quality components, this in-depth guide is designed to help engineers, procurement professionals, and buyers make informed decisions.
Types of Toroidal Coils
There are several categories of toroidal coils, each tailored to specific use cases and technical requirements. The differences among toroidal coil types stem from the choice of core materials, construction techniques, and their resulting electrical and magnetic properties. Understanding these distinctions is essential when evaluating toroidal coil suppliers or selecting the right component for your application.
Ferrite Core Toroids
Ferrite core toroidal coils are manufactured from ceramic materials combined with metal oxides. The core typically contains iron oxide mixed with metals such as copper, cobalt, zinc, nickel, and manganese. The two most widely used ferrite materials in toroidal inductors are manganese-zinc ferrite and nickel-zinc ferrite.
Ferrite toroids are highly valued in the electronics industry for their moderately low magnetic permeability and low saturation flux density. Their high electrical resistivity makes them ideal for reducing eddy current losses, which is crucial for high-frequency circuit applications including power supplies, EMI filters, and signal transformers. Ferrite toroidal cores are a preferred choice in consumer electronics, industrial automation, and telecommunications due to their cost-effectiveness and efficient performance at a wide frequency range.

Powdered Metal Core Toroids
Powdered metal core toroidal coils are made from metallic powders—such as powdered iron, molybdenum permalloy, or carbonyl iron—blended with insulating binders. The powder is pressed into a toroidal shape, then heat-treated to achieve the desired magnetic properties.
These toroids demonstrate high saturation flux density, making them suitable for applications where current spikes and surges are frequent. Powdered iron toroids, for example, are widely used in switching power supplies, DC-DC converters, inverters, and RF (radio frequency) circuits, where stable inductance and minimal core losses are required. The ability to tailor the material blend allows engineers to optimize for specific requirements such as temperature stability, core loss, and frequency response.

Laminated Iron Alloy Toroids
Laminated iron alloy toroidal coils are commonly employed in low-to-medium frequency transformer applications. These cores are fabricated by rolling iron alloy into thin sheets (laminations), which are then stamped and insulated from each other. This laminated structure significantly reduces eddy current losses and improves efficiency in power transfer.
The two main materials used for laminated toroids are silicon iron alloy (for high-voltage transformers) and nickel-iron alloy (for high-frequency, low-loss applications). Typical use cases include audio transformers, distribution transformers, and industrial power conversion. When selecting a laminated toroidal coil, consider factors such as core thickness, insulation quality, and the specific electrical parameters of your system.

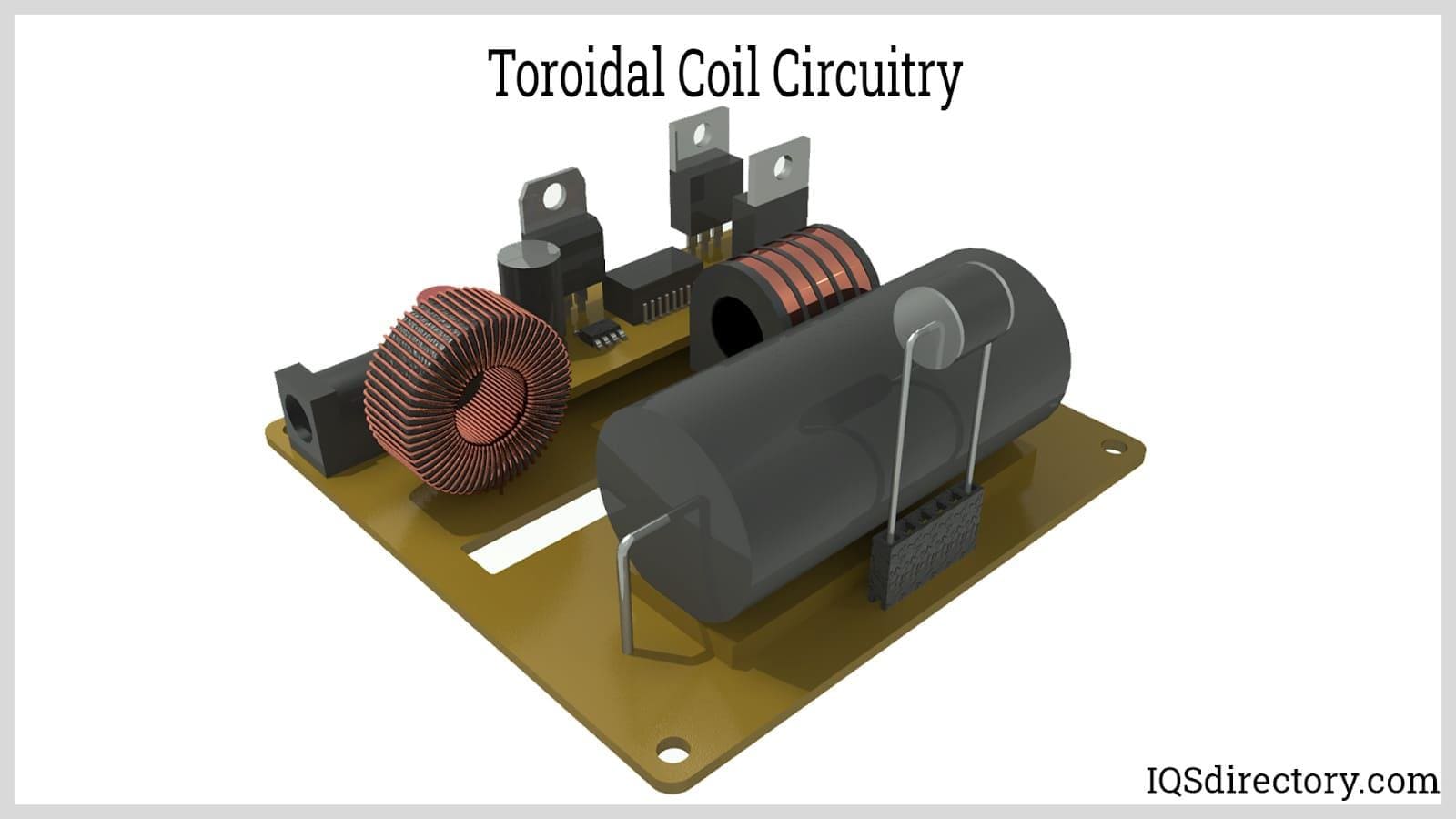
Tape Wound Core Toroids
Tape wound core toroids are constructed by winding insulated metallic ribbons into a spiral toroidal shape, as opposed to stacking individual laminations. The resulting core is then encapsulated in a thin layer of aluminum or plastic for protection and electrical insulation.
The tape wound construction yields superior magnetic performance at higher frequencies, making these toroids ideal for current transformers, precision power monitoring, pulse transformers, and specialized medical or scientific instrumentation. The tight winding and continuous ribbon structure minimizes losses and ensures stable operation under load.

Common Applications of Toroidal Coils
Due to their unique characteristics—such as efficient magnetic field containment, high inductance, and compact design—toroidal coils are integral to countless modern technologies. Here are some of the most common and high-value applications of toroidal inductors and transformers:
- Power Supplies and Converters: Toroidal transformers are the core of switch-mode power supplies (SMPS), DC-DC converters, inverters, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). Their high efficiency and low electromagnetic interference (EMI) make them ideal for sensitive electronics.
- Medical Equipment: Precision toroidal chokes and inductors are used in MRI machines, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory equipment where low noise and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) are vital.
- Telecommunications: Toroidal coils enable signal filtering, impedance matching, and noise suppression in telecommunication networks, base stations, and data transmission equipment.
- Audio Equipment and Musical Instruments: Low-distortion toroidal transformers are favored in amplifiers, mixing consoles, and high-end audio gear for their minimal hum and superior fidelity.
- Industrial Automation: Used in motor drives, robotics, and PLCs (programmable logic controllers) for power isolation, voltage regulation, and electromagnetic compatibility.
- Nuclear Fusion and Research: In experimental reactors such as tokamaks, toroidal magnetic coils confine plasma during high-temperature fusion experiments.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Toroidal inductors help manage power conversion and noise filtering in solar inverters, wind turbine controllers, and battery energy storage systems.
Looking for Specific Toroidal Coil Applications?
What are the best toroidal coil solutions for renewable energy?
How do toroidal inductors improve audio quality in amplifiers?
Which toroidal transformers are recommended for medical imaging equipment?
Explore our detailed application guides to discover industry-specific use cases and technical recommendations for your project or manufacturing needs.
Advantages of Toroidal Coils
Choosing a toroidal coil design provides several technical and operational advantages over other inductor or transformer types. Here are the main benefits that make toroidal coils a preferred solution in advanced electronics and electrical engineering:
- High Flux Density: Toroidal coils can operate reliably at flux densities exceeding 14 kilogauss, surpassing conventional transformers (typically limited to 11–14 kilogauss). This translates to greater power handling in a smaller footprint.
- Superior Electromagnetic Compatibility: The closed-loop shape of the toroid core minimizes stray magnetic fields, reducing EMI and allowing toroidal transformers to be mounted closer to sensitive electronic circuits without risk of interference.
- Low Mechanical Hum and Acoustic Noise: The absence of air gaps in the core construction eliminates vibration and hum, which is essential for quiet operation in audio, medical, and laboratory environments.
- Compact Size and Flexible Mounting: Toroidal coils are smaller and lighter than comparable E-I core transformers, making them ideal for space-constrained designs and portable devices.
- Reliable Electrical Induction: The continuous winding and robust core reduce the risk of wire movement and mechanical failure, resulting in long service life and high dependability.
- Energy Efficiency: Less core loss and lower heat generation improve overall system efficiency and reduce cooling requirements.
- Customizability: Toroidal coils can be custom-wound to match specific voltage, current, and inductance requirements for specialized applications.

Disadvantages and Limitations of Toroidal Coils
Despite their many benefits, toroidal coils are not always the optimal choice for every project. Here are some important trade-offs and potential drawbacks to consider during your component selection process:
- Complex Manufacturing Process: Winding coils onto a toroidal core is labor-intensive and requires specialized machinery, resulting in higher production costs compared to standard core shapes.
- Sensitivity to Physical Stress: Toroidal coils can deform or suffer performance loss under mechanical stress or impact. Careful handling and secure mounting are necessary.
- Thermal Limitations: Sudden temperature fluctuations and extreme heat can cause core saturation or insulation failure, especially in high-power applications.
- Limited Availability in High-Volume, Low-Cost Markets: Due to their production complexity, toroidal coils may not be as cost-effective for high-volume, low-cost consumer devices.
- Design Constraints: Not all circuit topologies benefit from the toroidal form factor; in some cases, E-I or C-core transformers may be preferable.
Need help weighing the pros and cons of toroidal coils for your design? Contact our engineering team for expert advice on material selection, winding techniques, and suitability for your application.
Key Considerations When Sourcing Toroidal Coils
Selecting the right toroidal coil supplier is critical for ensuring quality, performance, and value. Whether you are a purchasing manager, design engineer, or OEM looking for custom toroidal transformers, consider the following factors when evaluating potential vendors:
- Material Expertise: Does the supplier offer a range of core materials (ferrite, iron powder, laminated, tape wound) and understand their implications for your application?
- Customization Capabilities: Can the manufacturer produce custom-wound toroidal coils to your exact electrical and mechanical specifications, including wire gauge, insulation, and mounting style?
- Quality Assurance: Are coils tested for inductance, resistance, core loss, and insulation breakdown under actual operating conditions? Look for suppliers with ISO or other relevant certifications.
- Production Capacity: Can the supplier scale from prototype batches to mass production without compromising lead times or product consistency?
- Industry Experience: Does the company have a track record in your market segment—such as medical, industrial, audio, or renewable energy applications?
- Technical Support: Are application engineers available to help with circuit design, troubleshooting, and regulatory compliance (such as UL, CE, or RoHS certification)?
- Transparent Pricing and Delivery: Does the vendor provide clear quotes, competitive pricing, and reliable delivery schedules?
How do you compare toroidal coil manufacturers?
What certifications should you request from a toroidal coil supplier?
How do material and winding choices affect cost and lead time?
How to Request Quotes and Compare Toroidal Coil Suppliers
To ensure a successful purchase, it's vital to compare several toroidal coil suppliers using a trusted directory or sourcing platform. Our directory of toroidal coil suppliers enables you to review detailed business profiles, areas of expertise, and key capabilities. Each toroidal coil manufacturer is featured with a dedicated profile page displaying their technical strengths, certifications, and application specialties.
Use our online RFQ (Request for Quote) form to quickly contact multiple toroidal coil companies with a single submission. You can specify technical requirements—such as inductance, voltage, current, frequency range, and compliance standards—to ensure apples-to-apples comparisons between quotes.
Questions to Ask When Choosing Your Toroidal Coil Supplier
- What core materials and winding techniques do you specialize in?
- Can you provide samples or prototypes for evaluation?
- What testing and quality control processes are in place?
- Do you have experience with our specific industry or regulatory standards?
- What is your typical lead time for custom orders?
- Are there minimum order quantities or flexible batch sizes?
Ready to start sourcing toroidal coils? Browse our supplier directory or request a quote now to connect with trusted manufacturers and streamline your procurement process.
Frequently Asked Questions About Toroidal Coils
- What is the difference between toroidal coils and E-I core transformers?
Toroidal coils offer higher energy efficiency, reduced EMI, and quieter operation compared to traditional E-I core transformers, but E-I cores may be preferable for certain cost-sensitive or high-power applications. - How do I choose the right core material for my toroidal inductor?
Consider your application's frequency range, power handling, size constraints, and environmental factors. Ferrite is ideal for high-frequency, low-loss needs; powdered iron for high current; laminated and tape wound for precision and low noise. - Can toroidal coils be customized for unique voltage or current requirements?
Yes. Most reputable suppliers offer custom winding, core selection, and insulation options to meet your exact electrical and mechanical specifications. - What are the main causes of toroidal coil failure?
Mechanical stress, thermal overload, improper winding, or poor insulation can lead to early failure. Sourcing from a quality-focused supplier and proper installation can mitigate these risks. - Where can I find technical support for toroidal coil integration?
Many suppliers offer engineering assistance, design guides, and compliance support for integrating toroidal coils into your products or systems.
Explore More Toroidal Coil Resources
Still have questions? Contact our experts for personalized recommendations or technical support as you evaluate or source your next batch of toroidal coils.










 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services